Overview of Sexually Transmitted Infections
Overview of Sexually Transmitted Infections
- What is Sexually Transmitted Infections (STI)/ Reproductive Tract Infections (RTI)
- Health problems caused by STIs/RTIs
- Common syndromes caused by infections that primarily affect the reproductive tract
- STI symptoms in men
- STI symptoms in women
- Common occurrence STIs/RTIs
- Prevention of STIs/RTIs
- Related Resources
What is Sexually Transmitted Infections (STI)/ Reproductive Tract Infections (RTI)
Sexually transmitted infections are infectious diseases that spread through unprotected sexual activity (without use of condom) with an infected partner. Agents of infection include bacteria, viruses and other micro-organisms that can enter a person’s urethra, vagina, mouth or anus.
Reproductive Tract Infections (RTIs) are infections that occur in the reproductive tract of both men and women. These are caused by bacteria, viruses or protozoa. RTIs include all infections of the reproductive tract whether transmitted sexually or not. The infection may come from the use of unhygienic toilets or faulty genital hygiene. RTIs may even occur due to imbalance of the normal bacteria in the reproductive tract.
Health problems caused by STIs/RTIs
The consequences of STIs/RTIs for reproductive health can be severe and life-threatening. They include Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), infertility (in women and men), ectopic pregnancy, and adverse pregnancy outcomes including miscarriage, stillbirth, preterm birth, and congenital infection. STIs/RTIs also increase the risk of HIV transmission.
Most STIs/RTIs can affect both men and women, although the consequences for women are more common and more severe than for men. In fact, STIs/RTIs and their complications are among the most important causes of illness and death for women in poor regions of the world.
STIs/RTIs also cause poor pregnancy outcomes. Infection within the placenta or amniotic sac (chorioamnionitis) due to endogenous or sexually transmitted organisms is a major cause of late spontaneous abortion and stillbirth. Infection may lead to prelabour rupture of membranes and preterm delivery.
Congenital infection due to syphilis, gonorrhoea, chlamydia, herpes simplex virus, hepatitis B and HIV can cause blindness, disability and death of the newborn.
Common syndromes caused by infections that primarily affect the reproductive tract
The following are some of the common syndromes caused by infections that primarily affect the reproductive tract. Some are sexually transmitted, others not. Some can be easily cured using antibiotics or other agents, while others are incurable. The table does not include STIs such as HIV and hepatitis B which are not clearly linked to one distinct syndrome.
|
Syndrome |
STI/RTI |
Organism |
Type |
Sexually transmitted |
Curable |
|
Genital ulcer |
Syphilis |
Treponema pallidum |
bacterial |
yes |
yes |
|
Chancroid |
Haemophilus ducreyi |
bacterial |
yes |
yes |
|
|
Herpes |
Herpes simplex virus (HSV2) |
viral |
yes |
no |
|
|
Granuloma inguinale (donovanosis) |
Klebsiella granulomatis |
bacterial |
yes |
yes |
|
|
Lymphogranuloma venereum |
Chlamydia trachomatis |
bacterial |
yes |
yes |
|
|
Discharge |
Bacterial vaginosis |
multiple |
bacterial |
no |
yes |
|
Yeast infection |
Candida albicans |
fungal |
no |
yes |
|
|
Gonorrhoea |
Neisseria gonorrhoeae |
bacterial |
yes |
yes |
|
|
Chlamydia |
Chlamydia trachomatis |
bacterial |
yes |
yes |
|
|
Trichomoniasis |
Trichomonas vaginalis |
protozoal |
yes |
yes |
|
|
Other |
Genital warts |
Human papilloma virus (HPV) |
virus |
yes |
no |
STI symptoms in men
- Discharge or pus from the penis
- Sores, blisters, Rashes or boils on the penis
- Lumps on or near the genital area or penis swelling in the genital area
- Pain or burning during urination
- Itching in and around the genital area
STI symptoms in women
- Pain in the lower abdomen
- Unusual and foul smelling discharge from the vagina
- Lumps on or near the genital area
- Pain or burning during the sexual intercourse
- Itching in and around the genitals
- Sores, blisters, Rashes or boils around the genitals
Women are more susceptible to infections. Correct and Consistent use of condom is the best way to prevent infection and it’s also important to take the full course and only stop medicines when told by doctor only.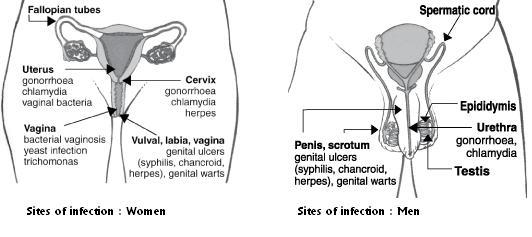
Common occurrence STIs/RTIs
STIs/RTIs are found worldwide but are more common in some areas. Transmission and prevalence (how common they are) are influenced by social and economic factors as well as by biology and behaviour. The burden of STIs/RTIs thus varies greatly from region to region, and from community to community. Where STIs/RTIs are common, so are their complications.
- STIs such as syphilis, gonorrhoea and chancroid spread more rapidly in places where communities are disrupted, migrant labour is common and commercial sex networks are active.
- Latrogenic infections are more common where there are many STIs, and where health care providers do not have the training or supplies to perform procedures safely. Postpartum and postabortion infections are more common where safe services and follow-up care are not available.
- Endogenous infections, such as yeast infection and bacterial vaginosis, are common worldwide and are influenced by environmental, hygienic, hormonal and other factors.
Prevention of STIs/RTIs
A comprehensive approach to STIs/RTIs includes prevention of sexually transmitted, iatrogenic and endogenous infections. STI prevention means reducing exposure—by using condoms and reducing numbers of sex partners. Condoms must be used correctly and consistently to prevent STI. Adolescents should receive support for decisions to delay sexual activity. The risk of iatrogenic infection can be reduced by good infection control procedures.
Source : Sexually transmitted and other reproductive tract infections - A guide to essential practice
Related Resources
Last Modified : 2/23/2020
This topic provides information related to steps t...
This topic provides information about Zero tillage...
This topic provides information about Causes, targ...
This topic provides about *99# Service- Innovative...
