Cirrohsis of Liver
Cirrohsis of Liver
Definition
Cirrhosis is the result of chronic liver disease that causes scarring of the liver and liver dysfunction. This often has many complications, including accumulation of fluid in the abdomen (ascites), bleeding disorders (coagulopathy), increased pressure in the blood vessels of the liver (portal hypertension), and confusion or a change in the level of consciousness (hepatic encephalopathy).
Alternative Names
Liver cirrhosis
Causes
Cirrhosis is caused by chronic liver disease, infection and long-term alcohol abuse (see Alcoholic liver disease). Other causes of cirrhosis include hepatitis B, medications, autoimmune inflammation of the liver, disorders of the drainage system of the liver (the biliary system).
Symptoms
- Ascites
- Swelling of the legs
- Vomiting blood
- Confusion
- Jaundice
- Small, red spider-like blood vessels on the skin
- Weakness
- Weight loss
- Nausea and vomiting
- Impotence and loss of interest in sex
- Bleeding hemorrhoids
Additional symptoms that may be associated with this disease:
- Decreased urine output
- Overall swelling
- Pale or clay coloured stools
- Nosebleed or bleeding gums
- Gynecomastia (breast development in males)
- Abdominal pain
- Abdominal indigestion
- Fevers
Symptoms may develop gradually, or there may be no symptoms.
Exams and Tests
A physical examination may reveal an enlarged liver or spleen, distended abdomen, yellow eyes or skin (jaundice), red spider-like blood vessels on the skin, excess breast tissue, small testicles in men, reddened palms, contracted fingers, or dilated abdominal wall veins.
- Tests can reveal liver problems including:
- Anaemia
- Coagulation abnormalities
- Elevated liver enzymes
- Elevated bilirubin
- Serum albumin low
- Enlarged liver (seen with an abdominal x-ray)
- A liver biopsy confirms cirrhosis.
Prevention
Don't drink heavily. If you find that your drinking is getting out of hand, seek professional help. Avoiding intravenous drug use (or only using clean needles and never sharing other equipment) will reduce the risk of hepatitis B and C. Some research indicates that hepatitis C may be spread via shared use of straws or items used to snort cocaine or other drugs. Avoid snorting drugs or sharing any related paraphernalia.
Illustrations and Images
Digestive system organs
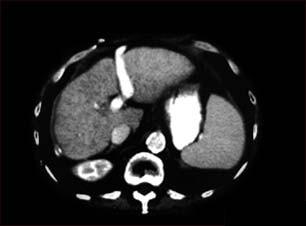
Liver cirrhosis, CT scan
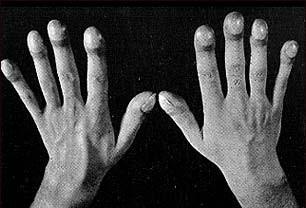
Clubbing symptom in patients with liver cirrhosis
Source: Portal Content Team
Last Modified : 2/20/2020
Acne causes, symptoms and remedies are described h...
Basic information on Malaria including symptoms, c...
Reasons for discharge from ear, symptoms and preca...
This topic deals with information related to Anima...
