Pea Insect Pests
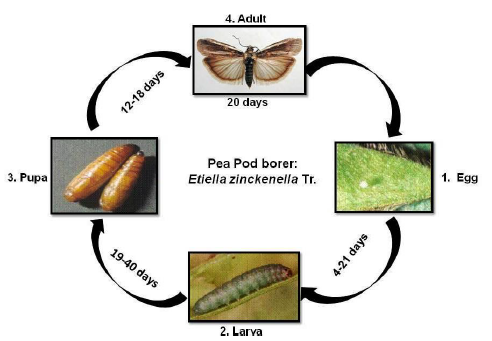
Pea pod borer
Etiella zinckenella Treitschke
Biology:
- Eggs: Development of egg lasts 4-21 days depending on weather conditions. Average fecundity is about 100-300, maximum 600 eggs.
- Larva: Coloration of larvae is variable, from dirty greenish-gray to reddish; body length 15- 22 mm and larval period is about 19-40 days depending upon weather conditions.
- Pupa: Pupa is brilliant, brown, fine punctured, to 7-10 mm in length; cocoon is thick, white, and usually covered with soil particles. Pupal period is about 12-18 days. Number of generations per year reaches three, though the third generation can be facultative. Overwinters as larva.
- Adults: Body length 8-11 mm, wingspan 19-27 mm. Wings longer than abdomen, folding as roof. Forewing is yellow- or greyish-brown with characteristic light stripe along fore edge, with orange spot on basal third, and with dark fringe. Hind wings are light gray, with dark venation and dark double line near fringe; the fringe is long and light in colour. Top of abdomen with a tuft of golden-yellow hairs. Life span of adult is 20 days
Life cycle:
Damage symptoms:
- Dropping of flowers and young pods
- As the larva develops within the pod, faeces accumulate causing soft, rotten patches on the pod.
- Seeds are either partially or entirely eaten, and considerable frass and silk are present.
- Older pods marked with a brown spot where a larvae has entered

Parasitoids:
- Egg parasitoids: Trichogrammatoidea armigera.
- Larval parasitoids: Bracon hebetor, Phanerotoma sp., Tetrastichus sp, Phanerotoma
Pod borer
Helicoverpa armigera Hübner
Biology:
- Egg: Gravid females lay eggs singly mostly on tender parts of the plants. Eggs are globular and shinning greenish yellow in colour. Incubation period ranges from3- 9 days depending upon weather conditions.
- Larva: Full grown larva is about 3.5 cm long. Larvas vary in colour, initially brown and later turn greenish with darker broken lines along the side of the body. The larval period lasts for 13- 19 days. Body covered with radiating hairs.
- Pupa: The full grown caterpillar pupates in the soil in an earthen cell and emerges in 16- 21 days. Pupation takes place inside the soil. Pupal stage lasts 7-15 days.
- Adult: Moth is stout, medium sized with brownish/grayish forewings with a dark cross band near outer margin and dark spots near costal margins, with a wing expense of 3.7
Life cycle

Damage symptoms:
- At early stage they feed on the foliage and sometime cause serious defoliation.
- During reproductive stage they bore the developing pod and feed on the seeds with its head typically thrust inside and most of the part of the body outside.
- Damaged pods are unfit for human consumption
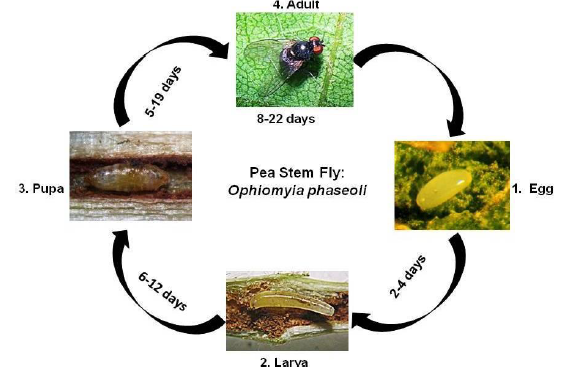
Stem fly
Helicoverpa armigera Hübner
Biology:
- Egg: The female lays 14-64· elongate, oval and white eggs singly into the leaf tissue with the help of its elongated ovipositor. The eggs hatch in 2-4 days
- Larva: Larva pass through three instars and the larval development is completed in 6-12 days.
- Pupa: The larva pupates within its gallery and the pupal period lasts 5-19 days.
- Adult: The adult flies are metallic black. They are active in summer and mate 2-6 days after emergence The female flies live for 8-22 days and the males for 11 days. The pest completes 8-9 generations.
Life cycle
Damage symptoms:
- The maggots bore into the stem thereby causing withering and ultimate drying of the affected shoots, thus reducing the bearing capacity of the host plants.
- The adults also cause damage by puncturing the leaves, and the injured parts turn yellow.
- The damage is more severe on seedlings than on the grown up plants.
Parasitoids of stem fly: Braconid wasp
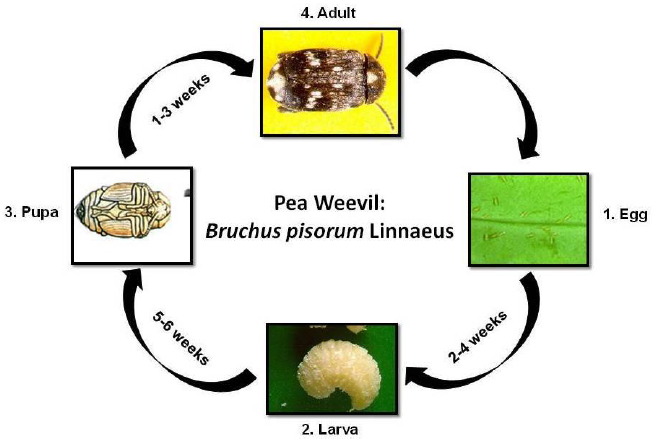
Pea Weevil
Biology:
- Egg: The egg is yellow, cigar-shaped and measures 1.5 mm by 0.6 mm.
- Larva: The larva is a legless, curled, cream grub which grows to about 5- 7 mm long.
- Pupa: Pupation takes place in inside the pods. The pupal stage lasts1-3 weeks depending upon season.
- Adult: The adult is a chunky beetle about 5 mm long, generally brownish flecked with white, black and grey patches. The tip of the abdomen extends beyond the wing covers and is white marked with two black oval spots.
Life cycle:
Damage symptoms:
- The larvae burrow straight through the pods to feed on the seed, so are not readily found for identification until seed is mature (above) and it is too late for control.

Parasitoids : Larval parasitoid: Dinarmus basalis
Pea aphid
Biology:
- Adult aphids are soft bodied, long legged, pear-shaped, green yellow or pink in colour with long conspicuous cornicles Both alate as well as apterous forms are present and these are generally females; males are rare.
- Reproduction is parthenogenetic and viviparous. It takes about a week to complete one generation and there are several overlapping generations in a year
Life cycle:

Damage symptoms:
- Both nymphs and adults suck the sap from young shoots, ventral surface of tender leaves, inflorescence and even on stems.
- Curling and distortion of leaves, stunting and malformation shoots occur.
- Leaves turn pale and dry. Honeydew secretion of aphids leads to sooty mould which hinders the photosynthetic activity of the plants.
- Parasitoids of aphids: Parasitic wasp, Aphadius sp., Aphalinus sp., Diaeretiella rapae
- Predators of pea aphids : Lacewing, ladybird beetles Predatory mite, Syrphid fly
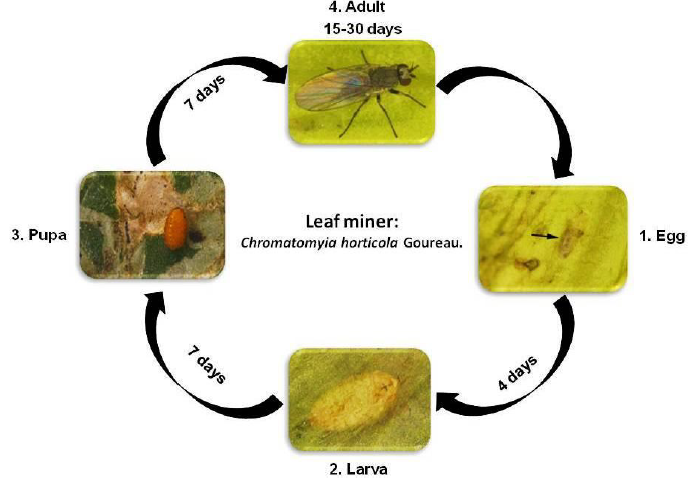
Leaf miner
Biology:
- Egg: Eggs are minute in size and orange yellow in colour. The egg hatches in 4 days.
- Larva: Apodous maggot feeds on chlorophyll mining in between epidermal layers. Full grown maggot measures 3 mm. Larval duration is about 7 days.
- Pupa: Pupation takes place inside a thin loose mesh of silken cocoon. Pupal period is about 7 days.
- Adult: It is a pale yellowish fly, measuring 1.5 mm in length. The female fly punctures upper surface of leaf to lay eggs singly. Total life cycle takes 3 weeks.
Life cycle:
Damage symptoms:
- The large number of tunnels made by the larvae between the lower and upper epidermis interferes with photosynthesis and proper growth of the plants, making them look unattractive.
- Leaves with serpentine mines
- Drying dropping of leaves in severe cases

Mining on leaves
Favourable conditions: Warm weather conditions are favourable for multiplication.
Natural enemies
- Parasitoids:
- Larval parasitoids : Chrysocharis pentheus, Diglyphus isaea,
- Larval and pupal parastioids : Gronotoma micromorpha, Neochrysocharis formosa
- Predators: Green lacewing, ladybird beetle, spider, red ant
IPM for Pea
To know the IPM practices for Pea, click here.
Source: NIPHM, Directorate of Plant Protection, Quarantine & Storage
Last Modified : 4/2/2020
This topic covers information about Fenugreek Ins...
This topic covers information about Broccoli Ins...
This topic covers the information related to Insec...
This topic covers information about Amla Insect Pe...
